
The following architectural visioning document was prepared as input for an activated carbon production center in southeast Georgia. The input includes a mass timber warehouse with an angled roof for solar, and a lab area outside the main building envelope using stacked shipping containers under a long side-roof for rainwater retention. The extended side acts as a buttress to the angled roof for additional stability during hurricane-force winds.


Stacked containers for residential apace amid controlled environment agriculture.

Angled roof for solar. Exterior framework could be avoided
by using nanowood as insulator for shipping containers.

Lightweight materials from superwood, transparent wood for windows, nanowood for insulation and water purification. Image source: Invent Wood
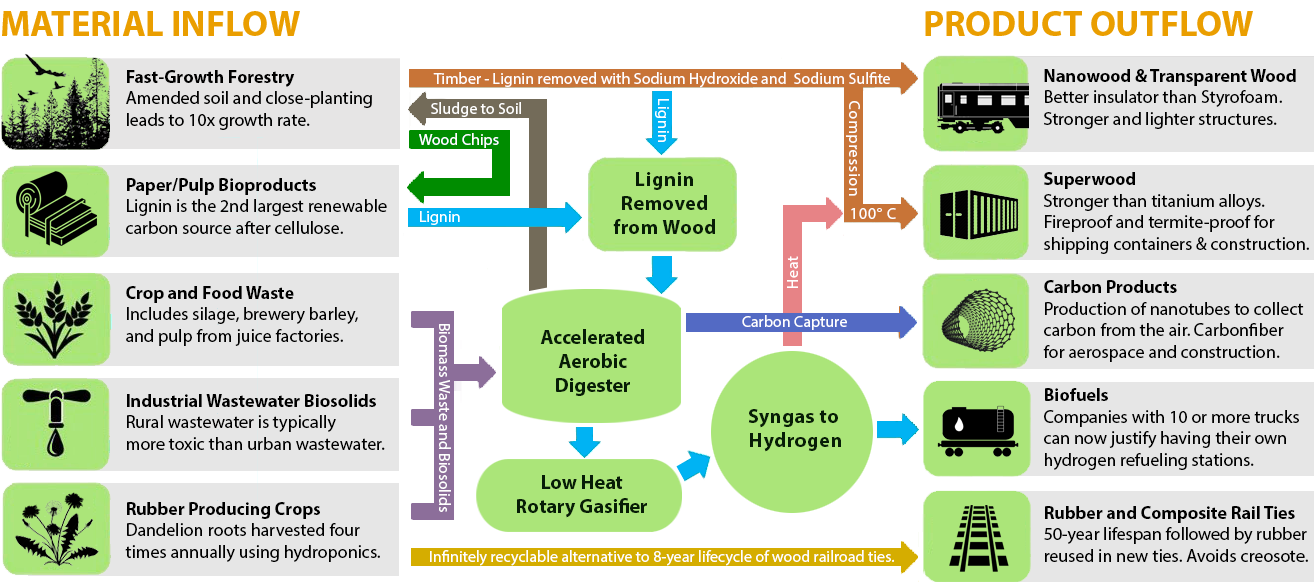
An Activated Carbon Study in 2016 found lignin provides a coconut-like activated carbon structure that is two to three times more valuable than activated carbon from wood.


How to reduce gas emissions from grazing animals - Over 95 percent of cow methane emissions are from the mouth as burps. Adding seaweed to feed cuts their emissions in half by aiding with fermentation.


Mass Timber and Bioconcrete Construction
Finnish Company plans $750M Georgia Factory for Mass-Produced, Modular Housing
Structural Mass Timber -
Mass Timber costs are comparible to steel construction, plus building with forestry products has the added advantage of easier modifications, improved performance and net positive carbon capture. Mass Timber has a higher Flash Flame Resistance (FFR) score than steel,
which is achieved by charring slightly during exposure to fire. This charring insulates the interior wood from further damage for a longer period of time than steel beams.
Solar Roof and Water Retention - The optimal angle of solar panels on south facing roofs and carports in the US south is around 30° - matching the location's latitude. Panels and rolled solar sheets can protect and extend the lifespan of roofing material beneath.
Solar Roof and Water Retention - The optimal angle of solar panels on south facing roofs and carports in the US south is around 30° - matching the location's latitude. Panels and rolled solar sheets can protect and extend the lifespan of roofing material beneath.

Integrating Containers with Warehouse Facades
- A row of 9.5' tall high-cube containers can provide portable production space and agricultural space.
A flat roof extending over containers expands surface area for solar and harvesting rain water.
Onsite waste-to-energy gassifiation processes could provide heat to produce superwood for shipping containers that are ligher and stronger than steel. Production of superwood requires compression while boiling the wood in hydrogen peroxide at 100º celsius to create new hydrogen bonds. About superwood
Onsite waste-to-energy gassifiation processes could provide heat to produce superwood for shipping containers that are ligher and stronger than steel. Production of superwood requires compression while boiling the wood in hydrogen peroxide at 100º celsius to create new hydrogen bonds. About superwood
Lightweight Superwood Containers and Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
Someday, freight containers produced from heat-treated superwood could provide lignin as a byproduct for the production of high value Activated Carbon (AC). More bioproducts from lignin.

Stacked containers for residential apace amid controlled environment agriculture.
Carbon-enriched soil and nutrient fluids can be used to grow plants during shipment in superwood freight containers built onsite.
• Bullet-proof superwood is fire resistant as a result of the increased density and reduced porosity.
• Safe bio-based flame retardant additives can also be added prior to the compression of superwood and transparent wood.

Angled roof for solar. Exterior framework could be avoided
by using nanowood as insulator for shipping containers.

Lightweight materials from superwood, transparent wood for windows, nanowood for insulation and water purification. Image source: Invent Wood
An Activated Carbon Study in 2016 found lignin provides a coconut-like activated carbon structure that is two to three times more valuable than activated carbon from wood.
more
Like coconut, lignin has tighter graphitic platelet spacings to remove more small molecules from drinking water. Activated carbon made from lignin is softer than from coconut shells, which allows it to be used as a powder for faster absorption of contaminants, with less water-leaching ash than present powdered activated carbons.Stacked Container Dwellings


How to reduce gas emissions from grazing animals - Over 95 percent of cow methane emissions are from the mouth as burps. Adding seaweed to feed cuts their emissions in half by aiding with fermentation.
Bioeconomies for Carbon Capture and Green Hydrogen Production

Hypothetical Superwood Container Dwellings
Lightweight, durable containers could be made of superwood, nanowood, transparent wood and carbon fiber.

Mass Timber and Bioconcrete Construction
Finnish Company plans $750M Georgia Factory for Mass-Produced, Modular Housing
